In 2009 the New Zealand Blood Service (NZBS) changed their deferral criteria for donating blood based on a 2008 review. The men who have sex with men (MSM) ban was reduced from 10 years to five years—“You must not give blood for: five years following oral or anal sex with or without a condom with another man (if you are male)”. There will be another review of the criteria in 2013.
Other deferral criteria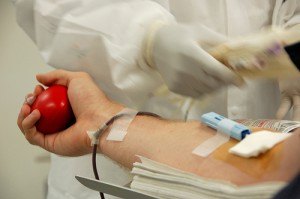
About 12% of people who try to donate blood are deferred. The NZBS has a full list of deferral criteria on their website.
A one year deferral is in place for a woman who has had sex with a MSM, and for those who have had sex with a person who carries the hepatitis B or C viruses, or an injecting drug user, a sex worker, a person with haemophilia or related condition, or with a person who has lived in or comes from a country with high HIV prevalence. People who have worked as sex workers only in New Zealand can’t give blood for a year.
People who have worked as sex workers outside of New Zealand or who have lived in a country with a high rate of HIV (including sub Saharan Africa and parts of Asia) can’t give blood for five years.
People who have injected/snorted non-prescription illegal drugs or who have lived in the UK, France or the Republic of Ireland for a total of six months or more between 1980 and 1996, because of possible exposure to Creutzfeld-Jakob disease, are permanently deferred from giving blood.
New Zealand sex workers aren’t considered to be a high HIV risk because: “there have been only 20 women diagnosed with HIV who were known to be sex workers and three to four men who were reported to be infected by a sex worker in New Zealand.”
MSM bans around the world
New Zealand isn’t as strict as other countries. Hong Kong, Singapore, Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Sweden and the UK have a lifetime ban on MSM donating blood. The US, Canada and Switzerland effectively do too, banning any men who have had sex with men after 1977.
Australia and Japan have a one year ban, South Africa has a six month ban, and Spain and Italy ban on behavior rather than the sex of sexual partners. Spain has a 12 month exclusion for anyone who has had more than one sexual partner in the last 12 months. The interpretation of Italy’s exclusion based on risky behavior is unclear and inconsistently applied—some centers still exclude MSM.
Blood safety
“Once a potential donor presents there is a three tier combination approach to safety: a questionnaire on behaviour followed by an interview, tests that are highly sensitive and specific are carried out on the donated blood, and (for manufactured plasma products) the use of physical and/or chemical methods to inactivate infectious agents.”
The HIV concerns that remain even though donated blood is tested relates to the early period following infection where the infection doesn’t show up on tests and relates to the risk that established infections aren’t picked up by testing or that infected blood is identified but fails to be removed from the system. The early “window period” for HIV averages to be about 12 days using Nucleic Acid Testing, which the NZBS tests with. A short deferral period of a year would eliminate the risk of window period infections. Longer deferral periods reduce the risk established infections present.
It’s thought that people with a higher risk of having HIV would also have a higher risk of having an “unknown or untested for infectious [agent]”.
The risk of the test system failing to detect an infection where “the marker is present” is very low because of the features of modern testing equipment used and because NZBS tests for each major virus twice. However “the test system may be unable to detect a rare form of the virus”.
“No transmissions have been documented in New Zealand since routine testing was introduced for these viruses… however… the low levels of risk are achieved by a combination of measures and are not solely due to the effect of blood donation testing.”
Australia’s one year deferral
About a decade ago, Australia dropped to a 12 month deferral for donors who have had male-to-male sex.
“Surprisingly in Australia, with a one-year deferral for MSM, though MSM are still over represented, the prevalence of HIV is only 4 per million donations, less than in New Zealand (11 per million donations). This suggests that there is either greater adherence to deferral criteria in Australia, or a higher rate of clinical HIV testing and therefore fewer undiagnosed infections, or the figures from Australia are incomplete.”
A study in Australia found there was no evidence of a significantly increased risk of transfusion-transmitted HIV subsequent to implementing the one year deferral period for MSM. In the one year deferral data the five MSM with HIV infections would have been excluded had they been honest and provided a complete history.
“We found no evidence that the implementation of the 12-month deferral for male-to-male sex resulted in an increased recipient risk for HIV in Australia. The risk of noncompliance to the revised deferral rather than its duration appears to be the most important modifier of overall risk.”
Harm
Donating blood is a valued social activity and the restriction based on sexual partners is indirectly homophobic which creates social exclusion and adds to stigma on the basis of male-to-male sex. In the US there is a group who have a “HIV prevalence 17 times that of their comparator: black versus white women”. There’s no call for a ban on that group from donating blood. Are we more sensitized to racism than homophobia?
“It does not distinguish between sexual acts… or whether a man has been in a monogamous relationship, but stigmatises any male same sex contact.”
But would a one year ban, like Australia’s, be any less discriminatory? There is an ethical requirement to protect the recipients of blood because they’ve been thrown into their situation. For indirect discrimination to be truly removed, there would have to be no ban on MSM. That’s unlikely until medical advances make it safe for the recipients of donated blood.
Image credit: Dave Herholz
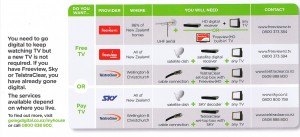
 New Zealand’s analog television is being turned off from 2012 so an advertising campaign has been set up to encourage people to switch over to digital. We were sent the following flyer in the mail (click for a bigger version), with good intentions, but it is perhaps quite unhelpful.
New Zealand’s analog television is being turned off from 2012 so an advertising campaign has been set up to encourage people to switch over to digital. We were sent the following flyer in the mail (click for a bigger version), with good intentions, but it is perhaps quite unhelpful.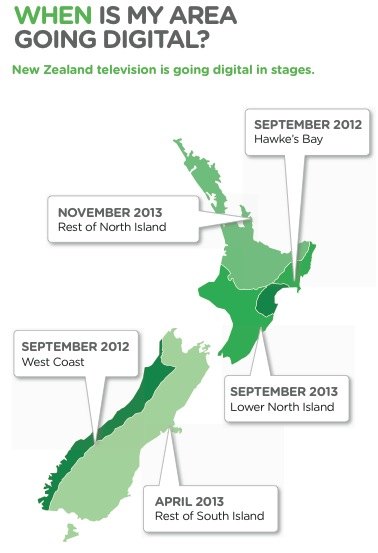


 We’re in the Green Zone. Here’s
We’re in the Green Zone. Here’s 
 The story
The story Macsyna King cooperated with the police and was a prosecution witness, she hasn’t just decided to speak now. She isn’t profiting from the book either, Ian says: “Apart from sharing a Domino’s pizza during lunch, Macsyna has never received anything nor will she.” Ian will earn money for the book, but points out that researching and publishing a book takes time and money and that
Macsyna King cooperated with the police and was a prosecution witness, she hasn’t just decided to speak now. She isn’t profiting from the book either, Ian says: “Apart from sharing a Domino’s pizza during lunch, Macsyna has never received anything nor will she.” Ian will earn money for the book, but points out that researching and publishing a book takes time and money and that 
 A group of researchers have published a very interesting paper:
A group of researchers have published a very interesting paper: 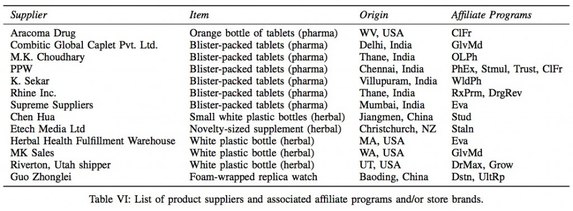
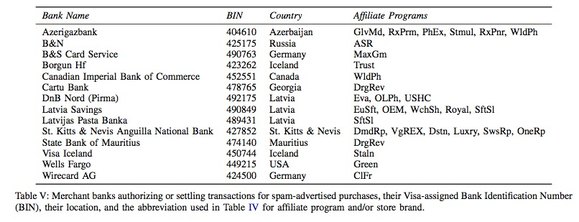 The researchers say that the banking/payment component of the spam value chain is the most critical. Payment infrastructure has “far fewer alternatives and far higher switching cost”.
The researchers say that the banking/payment component of the spam value chain is the most critical. Payment infrastructure has “far fewer alternatives and far higher switching cost”.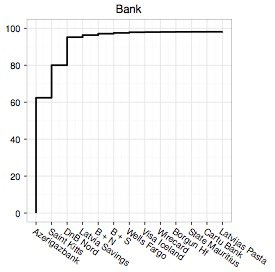
 The
The 
 National’s involvement
National’s involvement