Depending on whether you want MMP to stay or go.

(Click for larger versions)
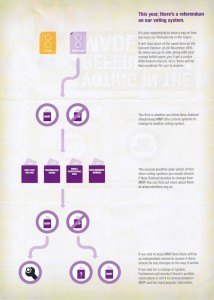
Alongside the general election this year on November 26th, voters will also be voting on whether they support the MMP voting system or would prefer to change to another system. There will be two parts to the referendum (both are optional, so someone could vote for neither parts, both parts, just the first part or just the second part):
- Should New Zealand keep the Mixed Member Proportional (MMP) voting system?
- I vote to keep the MMP voting system
- I vote to change to another voting system
- If New Zealand were to change to another voting system, which voting system would you choose?
- I would choose the First Past the Post system (FPP)
- I would choose the Preferential Voting system (PV)
- I would choose the Single Transferable Vote system (STV)
- I would choose the Supplementary Member system (SM)
If at least half of the voters vote to keep MMP, there will still be an Electoral Commission review of it in 2012. If at least half of the voters vote to change the voting system, Parliament will decide if there’s another referendum in 2014 (Stuff has reported it as 2016, but it’s 2014 on the Elections 2011 website) to choose between the most popular alternative (according to the second part of this referendum) or MMP.
STV is probably the only other roughly proportional voting system, with the number of MPs elected reflecting the total share of the party’s votes across the country. However some people might feel their STV vote is useless because if they are in an electorate that predominantly supports, say, National, their vote for a, say, Green MP won’t “count” towards the Green party at all unless the Green MP wins that electorate. MMP is still the best system and results in a proportional and representative Parliament.
It’s arguable that few people actually know how our current or past election systems work(ed), even after having them in place for years. No information explaining the different systems was included in the flowchart’s mail out, except saying that more information will be, I assume mailed out (what about the trees?!@11@), closer to election day and that information is also available on the Elections website. However, most people are inherently lazy and are unlikely to seek out additional information themselves. This will probably benefit the status quo.
Tweeting on election day
The Electoral Act prohibits “electioneering” on election day (midnight-7pm), meaning it’s illegal to distribute statements likely to influence voting decisions. The fine for electioneering on election day is up to $20,000. Chief Electoral Officer Robert Peden says that social networks (Twitter, Facebook…) are covered by the ban and will be checked on election day for influencing material. He says “For a long time, the law has allowed for campaign-free election days, and my sense is that New Zealanders like it that way and so it’s not really in people’s interest to do things like tweet and breach the rules.”
This is stupid.
Amanda Palmer quite accurately compares Twitter to a bar. It can be great and you can find some really interesting people using it, or sometimes you can have inane conversations about nothing. The bar analogy also works for how tweets are shared. Tweets are only “sent” to users that “opt in” to receiving them, just like someone opts in to a conversation in a bar. Maybe they overhear part of a conversation, or are aware of it because their friends are involved, but they can choose to ignore it or join in themselves. This is just like Twitter: you could be aware of a conversation or tweet because of search, through someone you’re following on Twitter, or looking at profiles, but you’re able to ignore the tweet, unfollow or block the users involved if you don’t like it.
Social networks are clearly different to someone erecting an election sign in their front yard and tweeting to a relatively small number of users who have opted in to receiving your tweets shouldn’t be considered ‘seeking to influence the public’ even if it is about who you’re supporting in the election.
In Canada, Twitter users are unhappy about a law that bans the premature transmission of election results—mentioning election results in Montreal in the east before the booths have closed in Vancouver in the west, with a fine of up to $25,000. Users of social networks realized that this applied to them and for their May 2nd election protested against the rule by tweeting the results of the election using the hashtag #tweettheresults.
It would be awesome if something like that happened here (but I obviously wouldn’t condone it).



